Livestock and poultry producers are key in helping to reduce the development and spread of antibiotic resistance. As well as the environment.
 Effects Of Antibiotics On Animal Feed Presentation
Effects Of Antibiotics On Animal Feed Presentation
However since total livestock biomass greatly exceeds that of human biomass total antibiotic use for humans is estimated to be much lower around 40000 tonnes in 2013.
Antibiotics and livestock. As of January 2017 all medically important antibiotics must be prescribed by a veterinarian. If the bacteria that colonize these animals acquire antibiotic resistance genes treatment becomes ineffective. Possible recommended alternatives to antibiotic use include probiotics and prebiotics competitive exclusion bacteriophages immunomodulators organic acids and teat sealants.
WHO is recommending that farmers and the food industry stop using antibiotics routinely to promote growth and prevent disease in healthy animals. The polypeptide antibiotic colistin is now also classified as a last-re-sort antibiotic for humans. Any time antibiotics are used in people and animals they can contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic Use in Livestock Production The use of antibiotics in livestock was introduced to treat microbial diseases just like in humans. Responsible use of antibiotics in animals lead to a decrease in bacteria. This means that the high volume of colistin 82 tonnes used in livestock farming is a cause for concern.
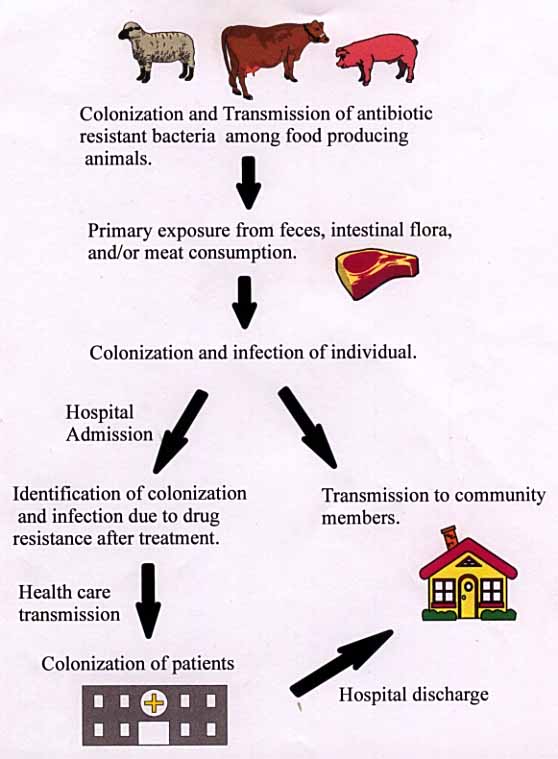
Oversight of antibiotic use in livestock and poultry production. Thus we have known definitively for more than 40 years that antibiotic usage in livestock results in the direct spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to humans. A veterinarians work is to ensure antibiotics are used responsibly to reduce the risk of resistance.
Antibiotics are added to. The bacteria capable of surviving the most antibiotics were the ones that grew and reproducedhelped by overuse and misuse of antibiotics in humans and livestock. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are also capable of spreading like any type of bacteria.
Thats a threat for the livestock sector because you cant keep your animals. The use of antibiotics to treat sick livestock is similar to that of humans. The antibiotics were used on farms to treat certain diseases if an event occurred.
A human or animal carrying an antibiotic-resistant infection can spread it to others. Antibiotics are valuable tools for treating infections in people and animals but any time antibiotics are used bacteria can develop antibiotic resistance. The One Health Commission.
Metaphylaxis therapy prophylaxis and growth promotion. The use of antibiotics is to ensure healthy livestock and protect human health. FDA has taken steps to expand the role of the veterinarian in managing antibiotics given to food-producing animals.
However to slow the spread of antibiotic resistance antibiotics should only be used when necessary. Antibiotic use in food animals can help treat bacterial diseases in animals. Antibiotic Use in the Livestock Industry.
In relative terms antibiotic use in livestock and humans is similar averaging 118 mgPCU population-corrected unit explained below and 133 mgkg respectively. Antibiotics are administered to the unhealthy animal at a therapeutic dose for a specific time period. The use of antibiotics to promote growth is still permitted in the USA and Asia.
However antimicrobials misuse in the livestock sector aquaculture and crop production is a major concern as a risk for emergence and spread of. Antimicrobial drugs are key in the treatment of diseases and their use is essential to protect both human and animal health. Using antibiotics in these situations is both necessary and in some cases required by law.
The first two use-cases are widely deemed as acceptable but the latter two are increasingly being touted as examples of misuse that may ultimately endanger human health. Using the drugs in this manner can allow animals to grow faster or more efficiently. There are several why antibiotics are administered to livestock.
In addition antibiotic use for growth promotion is being discontinued. The new policy dictates that antibiotic manufacturers will no longer market antibiotics for growth performance in livestock if those antibiotics are deemed medically important for. But reducing the use of antibiotics and applying measures to prevent the spread of infections could generate additional costs for farmers and.
Then antibiotics were used to control the spread of a disease within a herd which led to healthier herds. The Food and Drug Administration FDA is implementing a voluntary plan with industry to phase out the use of certain antibiotics for enhanced food production. Giving routine antibiotics to livestock has been sharply curtailed in the United States thanks to new rules by the Food and Drug Administration that went into effect on January 1.
In the ensuing decades numerous studies have been published in peer-reviewed scientific literature providing. NAMI and its members support FDAs. The new WHO recommendations aim to help preserve the effectiveness of antibiotics that are important for human medicine by reducing their unnecessary use in animals.
Antibiotics as growth promotors in livestock farming in 2006. In livestock production there are several antibiotics that are indicated or approved for use to improve feed efficiency or weight gain. Rethink livestock production systems to reduce inherent disease risk.
